After a strong Q1, fundraising by Greater China startups plunged in April-June (Q2) 2024 to levels seen during the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020—a sign of low confidence among private market investors.
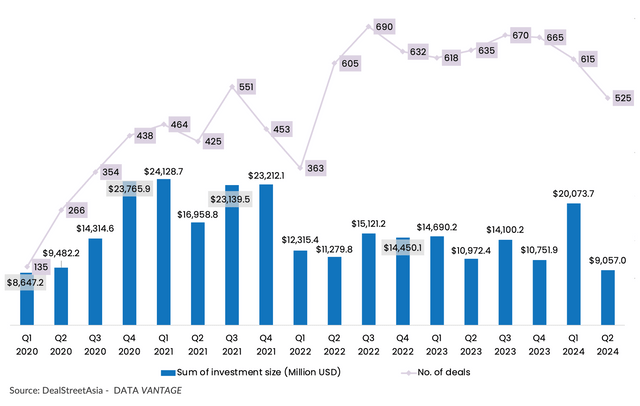
Capital raised by startups headquartered in mainland China, Hong Kong, Taiwan, and Macau just crossed $9 billion in Q2, down 54.9% quarter-on-quarter (QoQ). Deal volume declined by 14.6% from the previous quarter to 525, signalling an active market but with more deals of smaller sizes, according to DealStreetAsia DATA VANTAGE’s latest report Greater China Deal Review: Q2 2024.
On a year-on-year (YoY) basis, Q2’s fundraising sum was down by 17.5%, while the deal count dropped by 17.3% from the same period in 2023.
Funds raised by Greater China startups
As global investors remain cautious about new capital deployments, Chinese state-backed investors have stepped in to back more homegrown startups. These include Chinese conglomerate Legend Holdings—Q2’s most active investor participating in 12 deals—and CICC Capital, which bankrolled eight startups in the quarter. However, their largely RMB-dominated investment efforts are not enough to offset the retreat of foreign capital.
“US LPs still comprise a large portion of China’s venture universe. If USD fundraising diminishes sharply, I don’t think RMB will be able to bridge the gap,” said Ray Hu, Founder & Managing Partner, of Blue Lake Capital.
Dealmaking remained sluggish in January-June (H1) with the completion of 1,140 deals, down 9% from 1,253 in the same period last year.
Mega deal value in Q2 more than halves
Investors have applied the brakes on billion-dollar deals, resulting in a significant drop in the combined value of Q2’s mega deals.
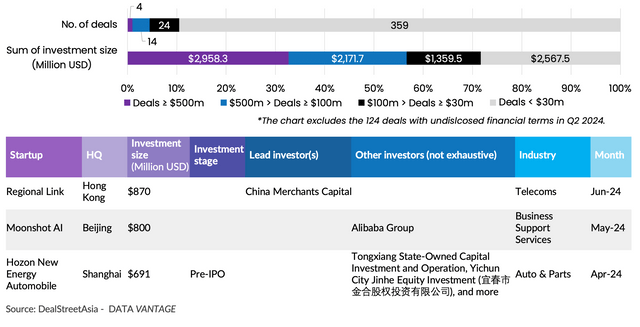
The quarter saw 18 mega deals, or transactions worth at least $100 million, collectively raising over $5.1 billion. With zero billion-dollar investments, their fundraising sum was down 64.9% from Q1, when there were three billion-dollar transactions including a PAG-led, $8.3-billion deal in shopping mall operator Newland Commercial Management.
Regional Link, a subsidiary of Hong Kong billionaire Richard Li’s telecom group PCCW, sold a 40% stake to China Merchants Capital for $870 million to become the biggest fundraiser in Q2.
It was followed by companies like generative artificial intelligence (GenAI) startup Moonshot AI and electric vehicle (EV) maker Hozon New Energy Automobile, which closed sizeable deals at $800 million and $691 million, respectively.
18 mega deals rake in 56.6% of the total financing in Q2
Late-stage, big-ticket dealmaking may maintain a tepid pace in the near term amid a tough exit environment and China’s move to tighten scrutiny of onshore listings.
In H1, only 16 companies closed their Series E and later rounds, accounting for just 1.4% of the total number of successful fundraisers. In comparison, Series A and earlier startups dominated, with the completion of 588 deals, or 51.6% of the half-year deal count.
Hong Kong IPOs set to rebound amid onshore listing slowdown
Macro market uncertainties and heightened rules for domestic listings have been weighing on the near-term IPO prospects of Greater China companies. Beijing’s introduction of the new ‘Nine National Articles’ in April could lead to more caution around near-term plans for an onshore listing, although the regulations are expected to bring in more quality issuers in the long run.
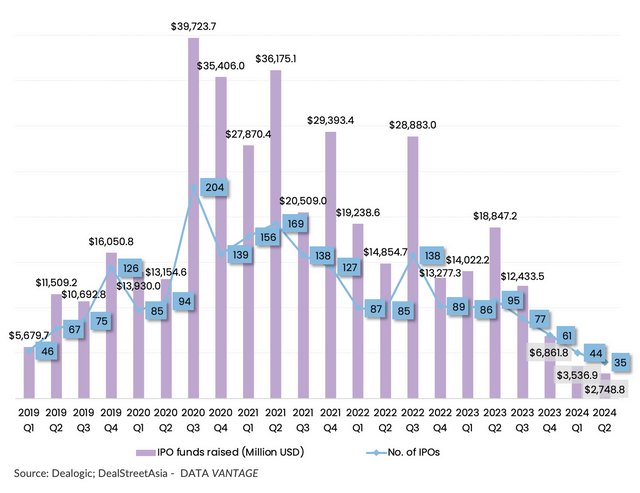
Q2 saw the number of IPOs by Greater China companies slide further to just 35 public share sales that raised about $2.7 billion, the lowest in both volume and total proceeds in at least five years, according to Dealogic data analysed by DealStreetAsia.
Throughout January-June, 79 Greater China IPOs raised less than $6.3 billion in total proceeds, representing sharp YoY declines of 56.4% and 80.9%, respectively.
IPO activity by Greater China firms slides to a historic low in Q2
Outside of mainland China, IPOs in Hong Kong are expected to rebound in H2 amid improving liquidity and market valuations. China’s pledge to speed up approvals for offshore listings and the successful IPO of QuantumPharm Inc in June, under the new Chapter 18C regime, could attract more tech issuers to the city.
Hong Kong’s main board was the most favoured exchange among Greater China issuers. The bourse welcomed 29 Greater China IPOs in H1, representing over one-third of the total IPOs by Greater China-based companies.
Meanwhile, the US capital market maintained its appeal to Chinese businesses, with the completion of 10 IPOs in the US by Greater China firms in H1, raising $568.2 million in proceeds.
As onshore listings came under increased scrutiny, more IPO candidates may pivot to the US. But geopolitical risks, the US Presidential election, and China’s data security rules would remain a hurdle to overseas listing efforts.
The Greater China Deal Review: Q2 2024 report has extensive data on:
- Quarterly and yearly startup fundraising trends
- Top deals of Q2 and H1 2024
- Most favoured industries by venture investors
- Top IPOs by Greater China firms in H1 2024 and pending large-cap IPOs
- Insights from prominent China-focused private market investors
The report is available exclusively to DealStreetAsia–DATA VANTAGE subscribers. Subscribe/upgrade your subscription now to access our entire set of reports. Still not sure? Opt for a one-month trial for only $249 or reach out to subs@dealstreetasia.com for a demo.